Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
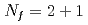 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 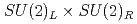 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 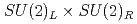 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 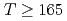 MeV.
MeV.
 anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperature
anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperatureAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(2), p.023B05_1 - 023B05_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The chiral susceptibility, or the first derivative of the chiral condensate with respect to the quark mass, is often used as a probe for the QCD phase transition since the chiral condensate is an order parameter of 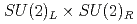 symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial
symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial  symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial
symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial  breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial
breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial  breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial
breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 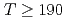 MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_23, 2021/06
The Casimir effect arises from the zero-point energy of particles in momentum space deformed by the existence of two parallel plates. For degrees of freedom on the lattice, its energy-momentum dispersion is determined so as to keep a periodicity within the Brillouin zone, so that its Casimir effect is modified. We study the properties of Casimir effect for lattice fermions, such as the naive fermion, Wilson fermion, and overlap fermion based on the M bius domain-wall fermion formulation, in the
bius domain-wall fermion formulation, in the 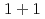 ,
, 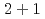 , and
, and 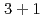 dimensional spacetime with the periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. An oscillatory behavior of Casimir energy between odd and even lattice size is induced by the contribution of ultraviolet-momentum (doubler) modes, which realizes in the naive fermion, Wilson fermion in a negative mass, and overlap fermions with a large domain-wall height. Our findings can be experimentally observed in condensed matter systems such as topological insulators and also numerically measured in lattice simulations.
dimensional spacetime with the periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. An oscillatory behavior of Casimir energy between odd and even lattice size is induced by the contribution of ultraviolet-momentum (doubler) modes, which realizes in the naive fermion, Wilson fermion in a negative mass, and overlap fermions with a large domain-wall height. Our findings can be experimentally observed in condensed matter systems such as topological insulators and also numerically measured in lattice simulations.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 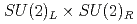 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 809, p.135713_1 - 135713_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:75.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a definition of the Casimir energy for free lattice fermions. From this definition, we study the Casimir effects for the massless or massive naive fermion, Wilson fermion, and (M bius) domain-wall fermion in 1+1 dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of
bius) domain-wall fermion in 1+1 dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of 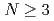 , the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M
, the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.
bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.
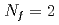 lattice QCD
lattice QCDSuzuki, Kei; Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.178_1 - 178_7, 2020/08
We investigate the high-temperature phase of QCD using lattice QCD simulations with 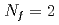 dynamical M
dynamical M bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial
bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial  symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M
symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial
bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial  anomaly at temperatures
anomaly at temperatures  220 MeV.
220 MeV.
Rohrhofer, C.*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Gattringer, C.*; Glozman, L. Ya.*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Lang, C. B.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.227_1 - 227_7, 2020/08
Properties of QCD matter change significantly around the chiral crossover temperature, and the effects on 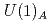 and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial
and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial 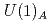 symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent
symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent 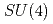 and
and 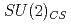 symmetries is discussed.
symmetries is discussed.
 Cu
Cu O
O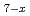 and its superconductive phase transition
and its superconductive phase transitionSuzuki, Takuya*; Takano, Hidekazu*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Kentaro*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Yoshio*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 36, p.249 - 257, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 30(1), p.51 - 54, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
 crystals
crystalsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Mizuki, Junichiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 43(9B), p.6821 - 6824, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.39(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 crystal
crystalYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(4), p.1050 - 1053, 2004/04
We have observed 90  C domain walls in a bulk BaTiO
C domain walls in a bulk BaTiO crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO
crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90
multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90  C domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO
C domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
 crystal
crystalYoneda, Yasuhiro; Komura, Yoshiki*; Suzuki, Yoshio*; Hamazaki, Shinichi*; Takashige, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(4), p.1050 - 1053, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have observed 90 domain walls in a bulk BaTiO
domain walls in a bulk BaTiO crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO
crystal by Synchrotron radiation topography, coupled with a CCD detector. The BaTiO multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90
multi-domain crystal was revealed to be strained at the 90 domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO
domain boundary. The polar direction of the BaTiO crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
crystal was tilted by this starin, and this strain also causes the irregular angle of the surface bending mode. The Synchrotron X-ray topography can be performed on a sample with electrodes. The topographic image of the ferroelectric doamin with an electric field clarified that the well-known stripe domain configuration can not be observed without a weak electric field due to the lattice strain at the doamin boundary.
 4 surface
4 surfaceTakahashi, Masamitsu; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yamamoto, Naomasa*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Physical Review B, 68(8), p.085321_1 - 085321_5, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The  ,
,  and
and  phases of the GaAs(001)-2
phases of the GaAs(001)-2 4 surface have been investigated by
4 surface have been investigated by  surface X-ray diffraction in an As flux and at temperatures ranging from 480
surface X-ray diffraction in an As flux and at temperatures ranging from 480 C to 610
C to 610 C. It has been found that the fractional-order peaks originating from the fourfold symmetry show shift in the [110] direction as well as significant broadening of the peaks in the
C. It has been found that the fractional-order peaks originating from the fourfold symmetry show shift in the [110] direction as well as significant broadening of the peaks in the  and
and  phases. The direction of the peak shift is characteristic in each phase. This behavior is explained by the formation of the antiphase domain boundaries. The atomic structure of the domain boundaries is discussed.
phases. The direction of the peak shift is characteristic in each phase. This behavior is explained by the formation of the antiphase domain boundaries. The atomic structure of the domain boundaries is discussed.
 by means of X-ray lasers
by means of X-ray lasersTai, R.; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Kishimoto, Maki; Tanaka, Momoko; Sukegawa, Kota*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Kado, Masataka; Lu, P.; Nagashima, Keisuke; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 89(25), p.257602_1 - 267602_4, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:81.12(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 )
) (BaTiO
(BaTiO )
) ]
] multilayer capacitor
multilayer capacitorYoneda, Yasuhiro; Sakaue, Kiyoshi*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 40(12), p.6888 - 6892, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.78(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 thin films
thin filmsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Sakaue, Kiyoshi*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 13(42), p.9575 - 9582, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:68.05(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
*; ; *
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213&214, p.676 - 681, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
; *
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 213-214, p.703 - 706, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.74(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
; *; *
Macromolecules, 27(26), p.7893 - 7906, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:105 Percentile:96.33(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English